Just like the MODE function, RANK is another useful statistical function in Google Sheets. Let me explain to you how to use the RANK Function in Google Sheets with one example.
While the MODE function returns the most commonly occurring number or date from a range, we can use the RANK function to find the rank of a number from a range. It’s so simple.
Example to RANK Function in Google Sheets
Syntax:
RANK(VALUE, DATA, [IS_ASCENDING])Here in this function, the value is the value of which the rank to be determined. Data means the array or range containing the dataset to consider.
The other element in the syntax, which is “is_ascending”, is entirely optional. It can decide whether to rank the highest or lowest value as 1. I think you can ignore this element as it’s irrelevant in most cases.
How to Use RANK Formula in Google Sheets
Please see the below example.
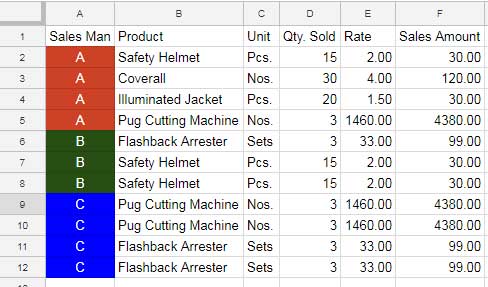
The above is a sample sales report. There are three salespersons, A, B, and C, and you can see their sales amount against each of their names.
How do we find the Rank of these salespersons based on their total sales (value)?
Summarising Data For Ranking
For that first, I summarise the data as below.
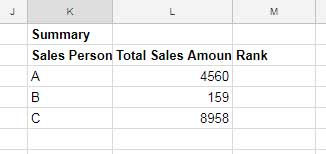
As a side note, I’ve just used the SUMIF function to summarise the data, though it’s not important here. We need the summary to understand the RANK function in Google Doc Spreadsheets.
You can see that there is one column I left blank in the above summary, and that is “Rank” (column M). The number of salespersons is only three here. So you can easily find the rank of salespersons.
Here salesperson “C” holds Rank # 1, “A” holds rank # 2, and “B” holds rank # 3.
Rank Formula
You can use a RANK formula to automate the ranking. It will be useful when the number of salespersons is large, and the sales values are flexible and may change at any time.
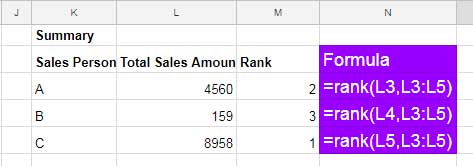
I am explaining the first formula. It applies to the subsequent two.
In the first formula, we first determine the rank of L3, i.e. 4560 against the range L3:L5. Similarly, the second and third formula has been used.
Hope you could understand the above use of the RANK function in Google Sheets.
Note:-
It seems the RANK.EQ function replaces the RANK function, and the latter is kept available for backward compatibility. So for more details, please check the former function guide.
Additional Resources:
- How to Find Rank of a Non-Existing Number in an Existing Data Range.
- Flexible Array Formula to Rank Without Duplicates in Google Sheets.
- How to Use the RANK.AVG Function in Google Sheets.
- How to Rank Group Wise in Google Sheets in Sorted or Unsorted Group.
- Top 10 Ranking without Duplicate Names in Google Sheets.
- The PERCENTRANK Functions in Google Sheets.
- Percentile Rank Wise Conditional Formatting in Google Sheets.