The INDEX function in Google Sheets is invaluable for retrieving cell contents based on row and column offsets. It becomes mighty when combined with other lookup functions like VLOOKUP, XLOOKUP, MATCH, or XMATCH.
This tutorial explains how to use the INDEX function to retrieve cell contents based on row and column offsets, as well as various dynamic range techniques.
We will demonstrate how to utilize these lookup functions in conjunction with INDEX for dynamic range techniques such as range slicing.
INDEX Function: Syntax and Arguments
Syntax:
INDEX(reference, [row], [column])The INDEX function has three arguments, with the first argument being mandatory and the others optional. Here’s an explanation of each:
reference: This is the cell range or array from which values are returned based on specified row and column offsets. If the optionalrowandcolumnarguments are not specified, it returns the entire range, making it a versatile alternative to the ARRAYFORMULA function.row: Optional. Specifies the row number within thereferencefrom which to return a value. The default is 0, which means no offset.column: Optional. Specifies the column number within thereferencefrom which to return a value. The default is 0, which means no offset.
You can better understand these arguments through the following examples of the INDEX formula, which focuses on its basic functionality.
Extracting Single Values with INDEX Function
We have sample data in the range A1:E, where A1:E1 contains headers. Cells A2:A contain sequential dates starting from June 1, 2024.
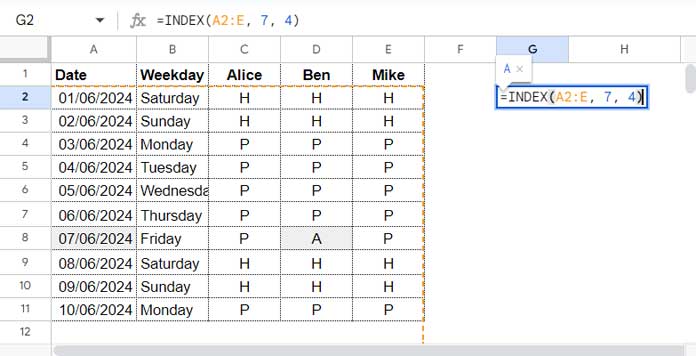
Since the dates are sequential and assuming they start in row 2, we can determine that the date 2024-06-07 is located in row 8 (index 7) of column A (A2:A).
You can use the following INDEX formula to retrieve the cell content in column D that corresponds to the date 2024-06-07 in column A:
=INDEX(A2:E, 7, 4)This formula retrieves the value from column D (4th column) where the date in column A is “2024-06-07”.
Returning Entire Rows or Columns with INDEX Function
Before the introduction of the CHOOSECOLS function, we typically used INDEX to extract specific columns from an array. The equivalent of extracting the second column using INDEX would be:
=INDEX(A2:E, 0, 2)This formula will return the entire second column (B) from the range A2:E.
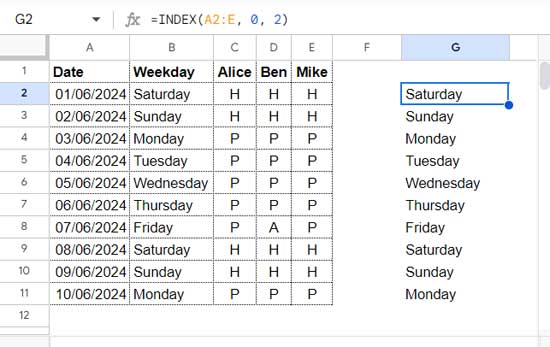
Similarly, before the introduction of CHOOSEROWS, we typically used the INDEX function to extract a specific row.
=INDEX(A2:E, 5) // returns the fifth row in the range A2:E.In the row and column arguments of the INDEX function, you can use either the MATCH or XMATCH functions to offset based on a lookup value.
For example, in the previous example, instead of specifying a row offset of 7, you can look up the date 2024-06-07 in column A using MATCH or XMATCH as follows:
=INDEX(A2:E, MATCH(DATE(2024, 6, 7), A2:A, 0), 4)
=INDEX(A2:E, XMATCH(DATE(2024, 6, 7), A2:A), 4)This technique is widely known as INDEX-MATCH in spreadsheet applications.
Example of Dynamic Range Slicing Using the INDEX Function
If you want to slice the data based on dynamic row offsets, you can use the following formula:
=INDEX(A1:E, XMATCH("Sunday", B1:B, 0 , -1)):INDEX(A1:E, XMATCH("?*", B1:B, 2, -1))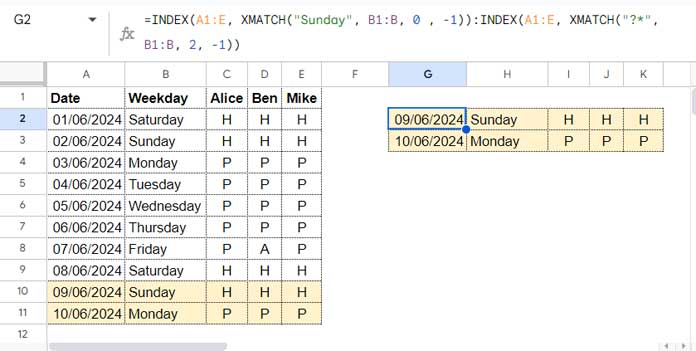
Here, two INDEX functions act as the starting and ending points of the range reference:
INDEX(A1:E, XMATCH("Sunday", B1:B, 0, -1)): Matches the last occurrence of “Sunday” in column B and defines the starting point of the range.INDEX(A1:E, XMATCH("?*", B1:B, 2, -1)): Matches the last non-blank text in column B and defines the endpoint of the range.
Therefore, this formula slices the range from the last Sunday to the last non-blank cell in column B, including all columns (A to E) in the sliced data.
If you want data from B1:E instead of A1:E, replace A1:E in the INDEX reference with B1:E. This creates another possibility: you can look up values in one table and return values from another table, provided both tables share the same structure.
Common Errors in the INDEX Function
Below are the common errors that you may encounter when using the INDEX function in Google Sheets:
#NUMError: The row or column arguments are outside the specified range.#N/AError: This often occurs when using other functions within INDEX, such as INDEX-MATCH, where the match returns #N/A.#REFError: The ‘reference’ doesn’t exist, either because it was deleted or incorrectly specified.#VALUEError: Incorrectly specifying row or column offsets, such as using “ten” instead of “10”.
Resources
The following tutorials explore real-life scenarios using the INDEX function in Google Sheets.
- Case Sensitive Reverse Vlookup Using Index Match in Google Sheets
- Dynamic Index Column in Vlookup in Google Sheets
- Multiple Conditions in Index Match in Google Sheets
- Hyperlink to Index-Match Output in Google Sheets
- Index Filtered Range Based on Count in Google Sheets
- Index with Match for 2D Array Result in Google Sheets
- Index Match Every Nth Column in Google Sheets
- Drop Rows and Columns by Index Numbers in Google Sheets






















Hi Prashanth
Thanks for the quick reply.
How is the syntax for this to pull the data from all 3 sheets (many more in the future) in Data_Spreadsheet file?
I’ve tried this but it’s not working…
=iferror(ArrayFormula(vlookup(A2:A,Query(importrange("URL Here","{'Data_ Sheet1'!A2:H,'Data_ Sheet2'!A2:H,'Data_ Sheet3'!A2:H}"),"Select Col1,Col2,Col3,Col4,Col5,Col6,Col7 where Col8='X'",0),{2,3,4,5,6,7},0)))Thanks
Nessus
Hi, Nessus,
Multiple Importrange (each tab to be imported separately) can negatively affect the performance of your Sheet.
So better on your ‘Data_Spreadsheet’, in a new tab, combine the data in all sheets. I have already done that on your Sheet (tab name is ‘Combine’).
Formula:
=query({'Data_ Sheet1'!A1:H;'Data_ Sheet2'!A2:H;'Data_ Sheet3'!A2:H},"Select * where Col1 is not null",1)Then use the same formula (shared in my last reply) to import and Vlookup.
Do change the tab name in the formula to the new tab name that you have used to combine Sheets in ‘Data_Spreadsheet’.
I have already updated that formula too.
Best,
Hi Prashanth
This article gave me an idea for something that I thought was not possible.
I have a spreadsheet file (Data_Spreadsheet) from where I am pulling the data using Query and Importrange functions to another spreadsheet file (Target_Spreadsheet).
So, I was wondering… is it possible to place the imported data to corresponding rows in Target_Spreadsheet file based on the first column (ITEM NUMBER)???.
I have prepared some files with sample data for you to understand more easily what I want to accomplish…
Thank you in advance
Nessus
Hi,
I have one formula added on the “kvp” tab. I have used Vlookup, not Index Match.
=iferror(ArrayFormula(vlookup(A2:A,Query(importrange("URL Here","'Data_ Sheet1'!A2:H"),"Select Col1,Col2,Col3,Col4,Col5,Col6,Col7 where Col8='X'",0),{2,3,4,5,6,7},0)))Related Tutorial: How to Vlookup Importrange in Google Sheets.
See if that helps?
Best,