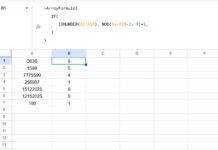
You can use two types of formulas to create a running total with structured table references in Google Sheets: Array Formula and Non-Array Formula.
Assume there is a column named ‘Data’ in a table. To get the running total of that column, you can use:
Non-Array Formula:
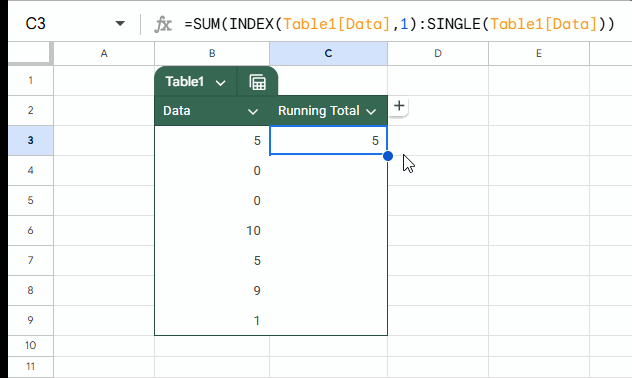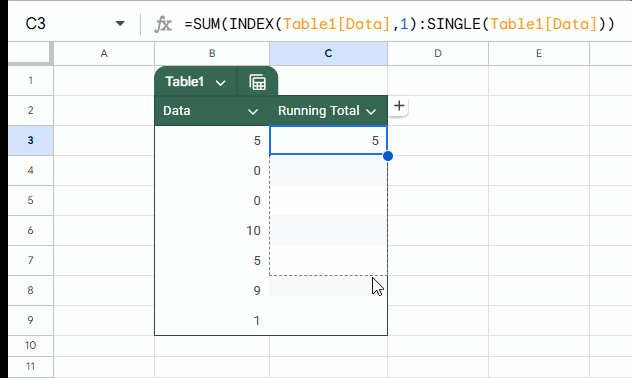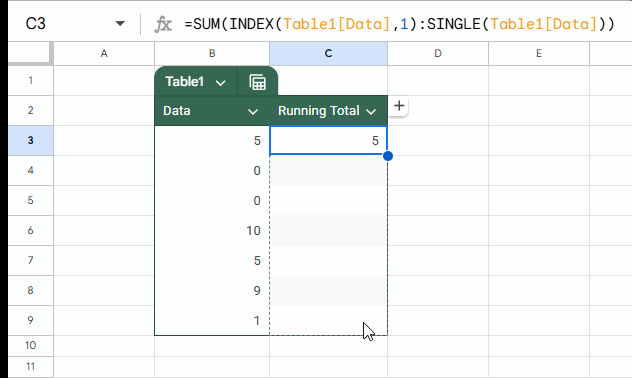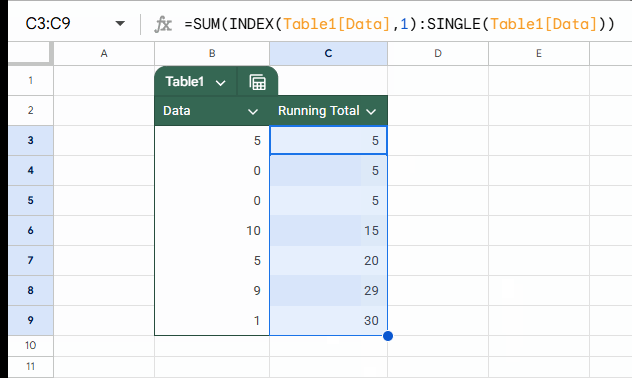
=SUM(INDEX(Table1[Data], 1):SINGLE(Table1[Data]))As per the sample data, you should enter this formula in cell C3 and drag it down to C9.
Array Formula:
Here you can use either the SCAN Lambda helper function or SUMIF.
As per the sample data, clear C3:C9 and enter one of the formulas below in cell C3:
=SCAN(0, Table1[Data], LAMBDA(a, r, a+r))=ArrayFormula(SUMIF(ROW(Table1[Data]), "<="&ROW(Table1[Data]), Table1[Data]))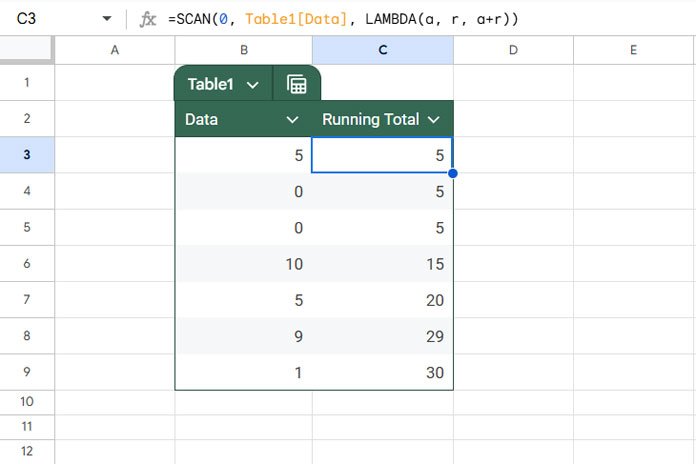
Both the array and non-array formulas have pros and cons. Before we dive into those, here is how the formulas work.
Drag-Down Formula Explanation
The syntax of the running total drag-down formula is as follows, whether you use structured table references or not:
=SUM(first:current)Where first is INDEX(Table1[Data], 1) and current is SINGLE(Table1[Data]).
Table1[Data] returns all data without the headers. We use INDEX to get the first value, which acts as both value and reference.
To get the current row value (reference), we wrap the entire column of data with the SINGLE function. This is equivalent to using @ in Excel, though @ won’t work in Google Sheets.
Array Formula Explanation
SCAN:
The SCAN function scans the array Table1[Data] and produces intermediate values stored in the accumulator, which is initially 0. It applies a LAMBDA function to each value:
LAMBDA(a, r, a+r)Where a is the defined name for the accumulator and r is the current row value. a+r means accumulator + current row value. The formula returns the accumulator value, which is the output of a+r for each row.
SUMIF:
The SUMIF function sums the range Table1[Data] where the row numbers of the range are less than or equal to the row numbers for each row. This generates a running total.
Running Total with Structured Table References: Things to Know
- If you use the running total array formula with structured table references, insert rows via the Insert menu. If you use the
+button in the table (visible when you hover your mouse pointer over the cells in the first column), you may encounter the error: “You cannot insert or delete cells over an array formula.” - When you use the
+button to insert a row below the last row, the non-array formula will not calculate the new row’s value automatically. Instead, you can enter a value below the table, which will automatically be included in the table. The formula will then calculate that value.
Resources
- Normal and Array Running Totals in Google Sheets
- Array Formula for Conditional Running Total in Google Sheets
- Reverse Running Total in Google Sheets (Array Formula)
- How to Calculate a Horizontal Running Total in Google Sheets
- Reset Running Total at Every Year Change in Google Sheets (SUMIF Based)
- Running Total by Category in Google Sheets (SUMIF Based)
- Running Total with Monthly Reset in Google Sheets (Array Formula)
- Weekly and Biweekly Running Totals in Google Sheets
- Reset Running Total at Blank Rows in Google Sheets
- Running Total with Multiple Subcategories in Google Sheets