The VAR is a statistical function in Google Sheets for calculating the variance of a sample. You can also use the function VAR.S for this. The letter ‘S’ in the latter function denotes ‘sample’.
When you compare both these statistical functions for the variance calculation, you can find that only the function names are different. All the arguments in these two functions are the same.
Then why there are two functions for variance calculation of a sample?
There are functions in Google Sheets for calculating the variance of an entire population. So from the function name VAR.S you can easily distinguish that the formula in use is for calculating the variance of a sample, not an entire population.
The VAR.S is a relatively new function that replaces VAR in Google Sheets. The function VAR is still there in Sheets as part of backward compatibility.
So I recommend using VAR.S instead of VAR function in Google Sheets.
Variance Calculation – How-To
We will discuss the use of the VAR function in Google Sheets later. Before that, let’s try to understand the ‘Variance’ calculation.
To understand variance, I think, we must first start with the standard deviation. Using the standard deviation, we can find how numbers are spread out.
Actually, the variance is the square of standard deviation or you can say standard deviation is the square root of the variance.
We can find the variance of an entire population by finding its squared differences from the mean and then average it. What about the variance of the sample then?
Example:
Let’s consider the height of 10 students (in centimeters) for manually calculating the variance. Later we can use the same data in the VAR function to calculate the variance.
| Student Names | Height (in cm) |
| A | 160 |
| B | 155 |
| C | 140 |
| D | 148 |
| E | 147 |
| F | 130 |
| G | 162 |
| H | 168 |
| I | 139 |
| J | 138 |
| Total | 1487 |
Steps:
First, calculate the average as below.
= 1487/10The output of the above formula would be 148.7. Then find the sum of squared difference from the mean.
Here is the formula to calculate the sum of squared difference from the average/mean.
=(160-148.7)^2+(155-148.7)^2+(140-148.7)^2+(148-148.7)^2+(147-148.7)^2+(130-148.7)^2+(162-148.7)^2+(168-148.7)^2+(139-148.7)^2+(138-148.7)^2Result: 1354.1
Variance of entire population = Sum_of_squared_differences_of_mean/N
In this, as per our example, the ‘N’ represents the number of students.
So the Variance is;
= 1354.1/10Result: 135.41
The variance of the sample is = Sum_of_squared_differences_of_mean/N-1
=1354.1/9Result: 150.46
By finding the square root of the above variance values, we can get the standard deviation of the sample as well as the entire population.
The VAR, as well as the VAR.S function, in Google Sheets, simplify the variance calculation for us.
Syntax of the VAR Function in Google Sheets
VAR(value1, [value2, ...])If you prefer to use the VAR.S instead, here is the syntax of the same. Again, please note that only the function name is different.
VAR.S(value1, [value2, …])Arguments
value1: The first value/range of the sample.
value2: It’s an optional argument. Additional values/ranges to include in the sample.
Even though from the second arguments onwards are optional, we can’t find the variance of a single value like =var(160).
The formula will return #DIV/0! error. But you can use a single range like =var(A1:A10).
Example to the Use of VAR Function in Google Sheets
Let’s find the variance of the height of 10 students in a class. For copying the sample data, please scroll up to find the table.
Note:- In cell B2, read the value as “Height in cm.”
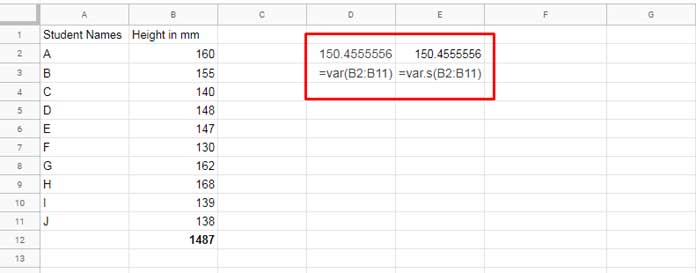
Both the VAR and VAR.S formulas in cell D2 and E2 respectively return the variance of the sample in column B as 150.46.
I have already explained to you how to calculate variance without the VAR or VAR.S function under the title ‘Variance Calculation (How to)’ above.
I hope, you could understand the use of the VAR function in Google Sheets and the calculation behind it.
Usage Notes
You must go through the following points to correctly use the VAR or VAR.S function in Google Sheets.
When you use a range/array as a value argument in VAR or VAR.S function, please do note the following points.
- If any cell is blank, the VAR function in Google Sheets ignores that.
- The function in Sheets includes 0 values in the calculation.
- If any cell in the range contains text, that cell will be considered as blank.
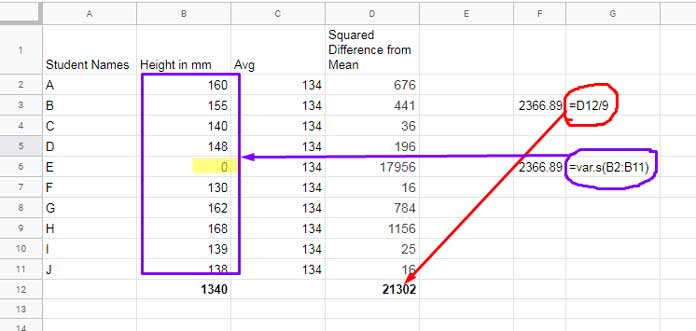
See the changes in the output of the formula when the value in cell B6 is either 0 or blank.
When the value in cell B6 is 0:
Note:- In cell B2 in both the screenshots below, read the value as “Height in cm.”
When the cell B6 is blank:
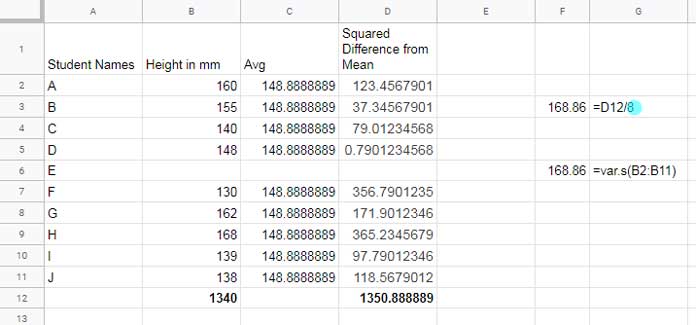
To make you understand the changes I have included two types of variance calculations in cells F3 and F6. I know the screenshot itself is self-explanatory.
That’s all on how to use the VAR function in Google Sheets. Enjoy!
Related Resources
- How to Use the STDEV Function in Google Sheets.
- Standard Deviation – DSTDEV Database Function in Google Sheets.
- Google Sheets Average Function [Advanced Tips and Tricks].
- DAVERAGE Function in Google Sheets – Formula Examples.
- How to Use the TRIMMEAN Function in Google Sheets.
- How to Use the HARMEAN Function in Google Sheets.
- GEOMEAN for Geometric Mean Calculation in Google Sheets.