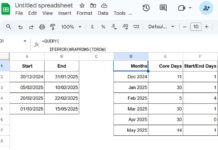
To sum every 7 rows, you can use either a drag-down formula or a dynamic array formula in Excel. This method is especially useful when you want to calculate weekly totals in a column that contains data entered in chronological order.
How to Use a Drag-Down Formula to Sum Every 7 Rows in Excel
If you prefer a drag-down formula, which is undoubtedly the simplest option, try this:
=SUM(OFFSET(range_start, (ROW(A1)-1)*7, 0, 7, 1))Replace range_start with the starting cell reference in absolute reference format (e.g., $B$2). No other changes are required.
Example:
Assume you have dates in column A (A2:A) and corresponding sales data in column B (B2:B). To calculate weekly totals, use the following formula in cell C2 and drag it down:
=SUM(OFFSET($B$2, (ROW(A1)-1)*7, 0, 7, 1))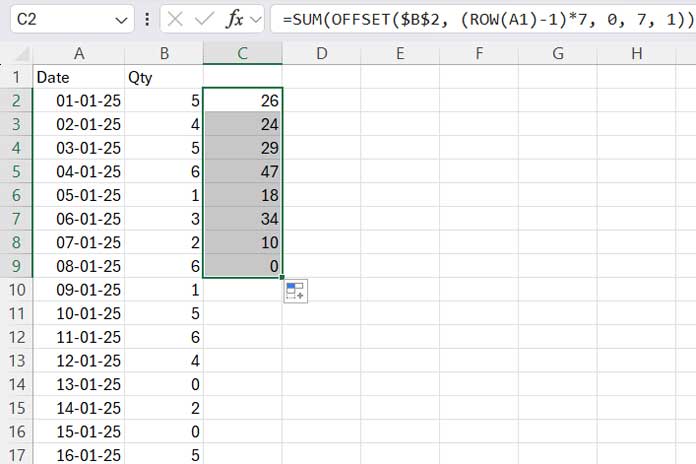
When applying this formula to a different dataset, replace $B$2 with the first cell reference of your range. You can leave A1 unchanged.
How the Formula Works:
The OFFSET function dynamically adjusts the range it sums based on the row number. The syntax is as follows:
=OFFSET(reference, rows, cols, [height], [width])reference:$B$2(starting cell of the range).rows:(ROW(A1)-1)*7(adjusts the starting point to sum every 7 rows: 0 rows, then 7 rows, then 14 rows, and so on).cols:0(no column offset, stays in columnB).height:7(sums 7 rows at a time).width:1(sums a single column).
Create a Dynamic Array Formula to Automatically Sum Every 7 Rows
If you want to sum every 7 rows in one go, use the MAP function, one of Excel’s powerful LAMBDA-based functions.
Example:
If the data is in B2:B50, enter this formula in cell C2:
=MAP(
SEQUENCE(ROUNDUP(ROWS(B2:B50)/7, 0), 1, 2, 7),
LAMBDA(x, SUM(FILTER(B2:B50, (ROW(B2:B50)>=x)*(ROW(B2:B50)<=x+6))))
)Using this formula to sum every 7 rows is simple. You just need to replace all occurrences of B2:B50 with your actual data range and adjust the number 2 (row number where the range starts) as needed. However, understanding the formula might seem complex because it involves nested functions like MAP and LAMBDA. Let’s break it down.
Formula Breakdown:
MAP Syntax:
=MAP(array1, lambda)array1: The input array on which the LAMBDA function operates.lambda: A custom function applied to each element inarray1.
In Our Formula:
array1:SEQUENCE(ROUNDUP(ROWS(B2:B50)/7, 0), 1, 2, 7)- Generates sequence numbers with a step value of 7, corresponding to the starting row of each 7-row block (e.g.,
{2; 9; 16; 23; 30; 37; 44}).
- Generates sequence numbers with a step value of 7, corresponding to the starting row of each 7-row block (e.g.,
lambda:LAMBDA(x, SUM(FILTER(B2:B50, (ROW(B2:B50)>=x)*(ROW(B2:B50)<=x+6))))- For each
xinarray1:FILTER(B2:B50, (ROW(B2:B50)>=x)*(ROW(B2:B50)<=x+6)): Filters rows betweenxandx+6.SUM: Totals the filtered rows.
- For each
In short, the MAP function applies the LAMBDA to each element in array1, returning the total of every 7 rows.