Formula compatibility issues can cause a #NAME “Unknown function” error in Sheets, particularly when switching from other compatible spreadsheet applications to Sheets. By introducing the MODE.SNGL function in Google Sheets, it appears that the Sheets development team is working to mitigate compatibility errors.
Google Sheets offers three functions for finding the mode, or the most frequently occurring number, in a dataset: MODE, MODE.MULT, and MODE.SNGL.
The MODE.SNGL and MODE functions are essentially similar in use. However, it’s uncertain whether the latter function will be deprecated in the future.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the MODE.SNGL function in Google Sheets. But what about MODE.MULT?
Sometimes, your dataset may contain multiple mode values. In such cases, you can utilize the MODE.MULT function.
Syntax and Arguments of the MODE.SNGL Function in Google Sheets
Syntax:
MODE.SNGL(value1, [value2, …])Function Arguments:
value1: The first value to consider when calculating a mode value.value2: The second value to consider when calculating a mode value.value3, value4, …: Additional values to consider.
“value1” is necessary, whereas “value2” and subsequent arguments are optional.
MODE.SNGL: Formula Examples
Example 1:
=MODE.SNGL(5, 4, 5) // returns 5In this example, three values (value1, value2, and value3) are used. Additionally, you can refer to range references in the MODE.SNGL function in Google Sheets.
Example 2:
=MODE.SNGL(A1:A10)Note:
- The MODE.SNGL function in Google Sheets is specified as taking a maximum of thirty arguments. However, Sheets supports an arbitrary number of arguments for this function.
- If you specify ranges, they can be of the same size or different sizes. For example,
value1(range 1) could be A1:A10 andvalue2(range 2) could be C1:C10 or C1:C50.
How Sorting Impacts MODE.SNGL Function Output
Sorting impacts the result because MODE.SNGL returns the first most frequently occurring number. When sorting your data ranges, it’s important to consider this.
Let’s see an example with both sorted and unsorted datasets:
The following formula utilizes an unsorted array as value1:
=MODE.SNGL({10; 4; 1; 5; 10; 5; 6}) // returns 10Now, let’s use the same array with the values sorted:
=MODE.SNGL({1; 4; 5; 5; 6; 10 ; 10}) // returns 5Additional Tip
The MODE.SNGL function arguments can include numbers, dates, times, and timestamps (DateTime). This means the function works equally well with date/time/DateTime ranges.
In the following example, value1 is the range A2:A, which contains timestamps. Please refer to the screenshot below for the formula and sample data.
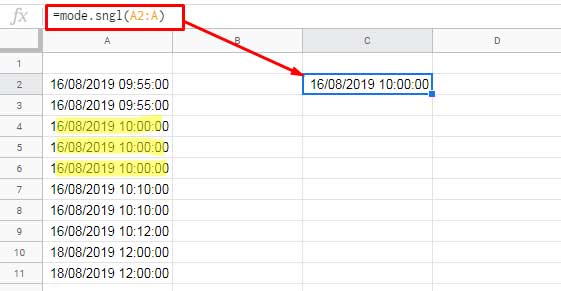
Cell C2 must be formatted to DateTime from the menu Format > Number > Date time.





















