Google Sheets offers two key financial functions for calculating loan interest: IPMT and ISPMT. In this tutorial, we’ll focus on how to use the ISPMT function. We’ll also briefly compare it with IPMT.
While IPMT stands for “interest payment,” it’s unclear what the “S” in ISPMT represents, but we will explore the difference between these two functions later.
ISPMT Function Syntax
Syntax:
ISPMT(rate, period, number_of_periods, present_value)Arguments:
- rate: The loan or investment’s interest rate.
- period: The specific period for which you want to calculate the interest.
- number_of_periods (Nper): Total number of payment periods.
- present_value (Pv): The current value of the loan or investment.
Usage Notes
Ensure the units for rate and number_of_periods are consistent. For example, with a 5-year loan at 10% annual interest and monthly payments, divide the rate by 12 and multiply Nper by 12.
ISPMT starts counting periods from zero, so if you want to calculate interest for period 1, adjust the period as shown below:
=ISPMT(10%, 1-1, 5, 20000)Using 1-1 is easier to remember than specifying 0 for period 1. Similarly, for period 10, you can specify 10-1 instead of 9 to avoid confusion. Ultimately, it’s up to you which method you prefer.
Example: Calculating Interest Payments
Monthly Interest Calculation (Periods 1 to 60)
Assume you take a $20,000 car loan at 10% annual interest for 5 years, with monthly payments:
| A | B | C | D | E |
| Loan Amount | $20,000 | |||
| Rate (Monthly) | 0.83% | =10%/12 | 1 | |
| Periods | 60 | =5*12 |
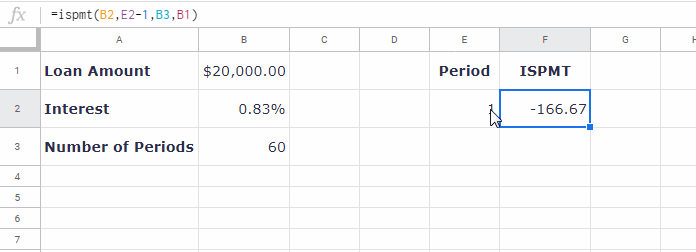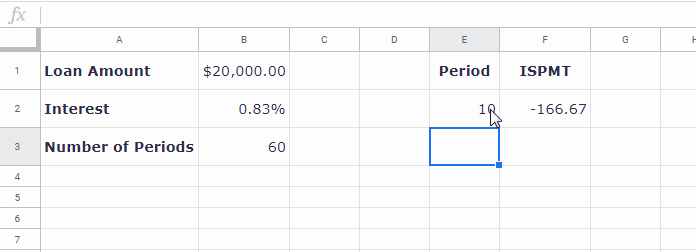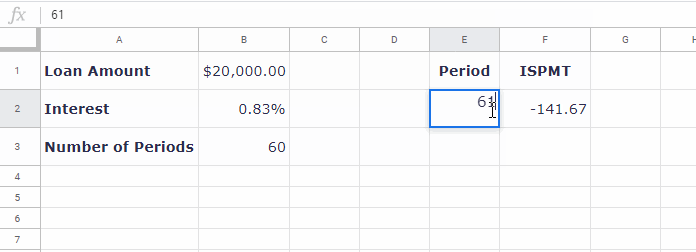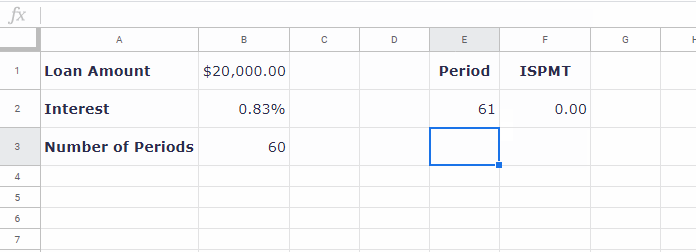
To calculate the interest for any month, use the formula:
=-ISPMT(B2, E2-1, B3, B1) // equivalent to =-ISPMT(0.83%, 1-1, 60, 20000)Change the period in E2 to see how the interest varies.
Yearly Interest Calculation (Periods 1 to 5)
For yearly payments over the 5-year term, use a similar formula but reference the year instead of months:
=-ISPMT($B$2, D3-1, $B$3, $B$1) // equivalent to =-ISPMT(10%, 1-1, 5, 20000)| A | B | C | D | E |
| Loan Amount | $20,000 | |||
| Rate (Monthly) | 10% | |||
| Periods | 5 | 1 |
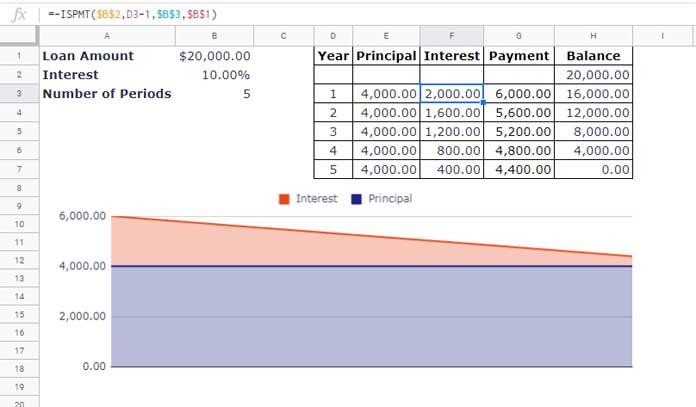
The formula returns an interest of -$2,000 for the first year.
ISPMT vs. IPMT
ISPMT: Use this function when the loan’s principal payments are equal across periods.
IPMT: Use this when your loan payments are fixed (equal periodic payments), but the principal portion varies over time.
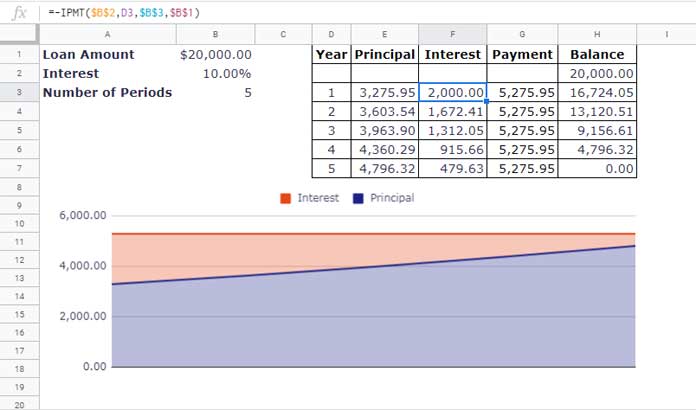
For loans with fixed periodic payments, you can calculate the principal portion using the PPMT function.
Conclusion
The ISPMT function is helpful when your loan schedule involves equal principal payments. For loans with fixed periodic payments, use IPMT. This distinction is crucial when choosing the right function for your financial calculations.





















